|
RAID 0 uses two or
more drives and stripes data across the drives without writing
any
parity data. The total capacity of the array is calculated by summing up the capacity
of each disk. As RAID 0
does not need to write parity blocks, it offers an increase in
performance. However, without any
parity blocks, RAID 0 provides no fault tolerance.
RAID 0 can be created
with hardware or software. RAID 0 is frequently used in
many
different
types of servers, external hard drives, NAS units, Snap Servers,
and in certain
desktop computers.
As the demand for storage capacity increases, hard drive
manufacturers are using RAID 0 to increase the overall capacity
of external hard drives.
For more
information about the devices using RAID 0 technology,
click here.
|
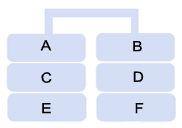
The following diagram
illustrates a RAID level 0: |
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
If you
experience problems with your RAID 0 array, please do not attempt
to correct the
problem
yourself. By taking matters into your own hands, you
could overwrite parity data
making RAID
recovery more difficult. Please follow
the steps below and contact ReWave
for assistance at
866-739-2835.
|
Turn off your RAID 0 array immediately.
This ensures that no additional data
can be written to the array, which could overwrite the data
you are trying to recover.
|
|
|
|
Document the events that occurred causing RAID
0 failure. Try to
make
notes documenting any problems that occurred and efforts
that were made to fix the
problems. If you remove
the drives from the array, it is
important to label the drives
with the same order in which
they existed in the array. Although not required, this
step will save us time during the RAID recovery process. |
|
|
|
Contact ReWave immediately. Our data recovery
team is available 24/7 to assist
you with RAID recovery at 866-739-2835. |
|
|
|